Treatments
Orthopedic Surgery
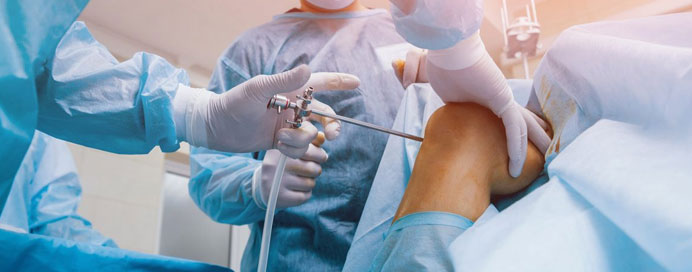
Orthopedic surgery focuses on diagnosing, treating, and repairing conditions related to bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Here are some core components:
Types of Orthopedic Surgeries
- Joint Replacement: Common for treating arthritis, especially in the knee and hip. Joint replacements involve replacing damaged parts with artificial implants.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where a small camera is inserted into the joint to diagnose or treat issues, often in the knee, shoulder, or hip.
- Fracture Repair: Using screws, plates, or rods to stabilize broken bones, aiding proper alignment and healing.
- Spinal Surgery: Procedures such as laminectomy or spinal fusion treat conditions like herniated discs, scoliosis, or spinal instability.
- Soft Tissue Repairs: Includes repairing tendons or ligaments, such as in ACL reconstruction or rotator cuff repair.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
- Benefits: Similar to other surgical fields, minimally invasive approaches in orthopedics (like arthroscopy) reduce recovery time, lessen pain, and decrease the risk of complications.
- Applications: These techniques are often used in joint surgeries, including knee, shoulder, and hip repairs, to minimize damage to surrounding tissues.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
- Preoperative Optimization: Evaluating the patient’s overall health, bone density, and alignment can help predict outcomes and prevent complications.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Critical to restoring mobility, strength, and range of motion. Physical therapy often starts shortly after surgery to optimize recovery.
- Pain Management: Tailored strategies, including medication, ice therapy, and alternative techniques, are used to control pain and facilitate healing.
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery
- Robotic Assistance: Increasingly used in joint replacement surgeries for more precise alignment and positioning.
- 3D Printing for Implants: Customized implants can be created for specific anatomical needs, improving joint replacement outcomes.
- Regenerative Medicine: Treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and stem cell therapy aim to promote natural healing and delay the need for surgery in some cases.
